# 线程池
池化技术的作用:把一些能够复用的东西(比如说连接、线程)放到初始化好的池中,便于资源统一管理。
# execute源码解析
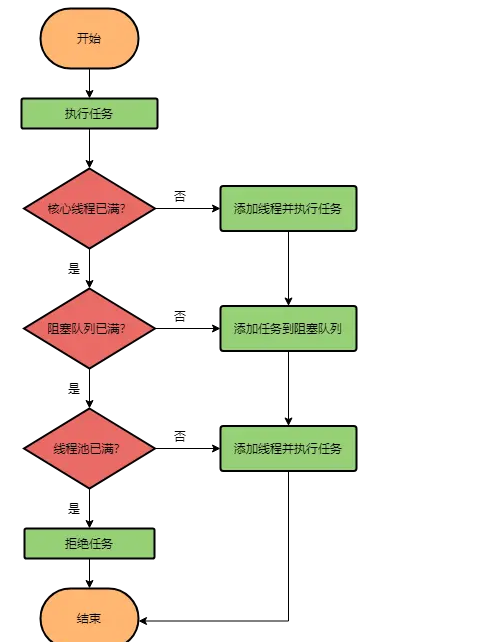
# execute()执行流程图
# 基础变量
// 使用原子操作类AtomicInteger的ctl变量,前3位记录线程池的状态,后29位记录线程数
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
// Integer的范围为[-2^31,2^31 -1], Integer.SIZE-3 =32-3= 29,用来辅助左移位运算
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
// 高三位用来存储线程池运行状态,其余位数表示线程池的容量
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// 线程池状态以常量值被存储在高三位中
// RUNNING状态其实就是全1
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS; // 线程池接受新任务并会处理阻塞队列中的任务
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS; // 线程池不接受新任务,但会处理阻塞队列中的任务
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS; // 线程池不接受新的任务且不会处理阻塞队列中的任务,并且会中断正在执行的任务
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS; // 所有任务都执行完成,且工作线程数为0,将调用terminated方法
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS; // 最终状态,为执行terminated()方法后的状态
// ctl变量的封箱拆箱相关的方法
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; } // 获取线程池运行状态
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; } // 获取线程池运行线程数
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; } // 获取ctl对象
private static boolean isRunning(int c) { return c < SHUTDOWN; } // 是否在运行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# 核心方法execute()
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null) // 任务为空,抛出NPE
throw new NullPointerException();
int c = ctl.get(); // 获取当前工作线程数和线程池运行状态(共32位,前3位为运行状态,后29位为运行线程数)
if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) { // 如果当前工作线程数小于核心线程数
if (addWorker(command, true)) // 在addWorker中创建工作线程并执行任务
return;
c = ctl.get();
}
// 核心线程数已满(工作线程数>核心线程数)才会走下面的逻辑
if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) { // 如果当前线程池状态为RUNNING,并且任务成功添加到阻塞队列
int recheck = ctl.get(); // 双重检查,因为从上次检查到进入此方法,线程池可能已成为SHUTDOWN状态
if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command)) // 如果当前线程池状态不是RUNNING则从队列删除任务
reject(command); // 执行拒绝策略
else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0) // 当线程池中的workerCount为0时,此时workQueue中还有待执行的任务,则新增一个addWorker,消费workqueue中的任务
addWorker(null, false);
}
// 阻塞队列已满才会走下面的逻辑
else if (!addWorker(command, false)) // 尝试增加工作线程执行command
// 如果当前线程池为SHUTDOWN状态或者线程池已饱和
reject(command); // 执行拒绝策略
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 添加worker
private boolean addWorker(Runnable firstTask, boolean core) {
retry: // 循环退出标志位
for (;;) { // 无限循环
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c); // 线程池状态
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN &&
! (rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null && ! workQueue.isEmpty()) // 换成更直观的条件语句
// (rs != SHUTDOWN || firstTask != null || workQueue.isEmpty())
)
// 返回false的条件就可以分解为:
//(1)线程池状态为STOP,TIDYING,TERMINATED
//(2)线程池状态为SHUTDOWN,且要执行的任务不为空
//(3)线程池状态为SHUTDOWN,且任务队列为空
return false;
// cas自旋增加线程个数
for (;;) {
int wc = workerCountOf(c); // 当前工作线程数
if (wc >= CAPACITY ||
wc >= (core ? corePoolSize : maximumPoolSize)) // 工作线程数>=线程池容量 || 工作线程数>=(核心线程数||最大线程数)
return false;
if (compareAndIncrementWorkerCount(c)) // 执行cas操作,添加线程个数
break retry; // 添加成功,退出外层循环
// 通过cas添加失败
c = ctl.get();
// 线程池状态是否变化,变化则跳到外层循环重试重新获取线程池状态,否者内层循环重新cas
if (runStateOf(c) != rs)
continue retry;
// else CAS failed due to workerCount change; retry inner loop
}
}
// 简单总结上面的CAS过程:
//(1)内层循环作用是使用cas增加线程个数,如果线程个数超限则返回false,否者进行cas
//(2)cas成功则退出双循环,否者cas失败了,要看当前线程池的状态是否变化了
//(3)如果变了,则重新进入外层循环重新获取线程池状态,否者重新进入内层循环继续进行cas
// 走到这里说明cas成功,线程数+1,但并未被执行
boolean workerStarted = false; // 工作线程调用start()方法标志
boolean workerAdded = false; // 工作线程被添加标志
Worker w = null;
try {
w = new Worker(firstTask); // 创建工作线程实例
final Thread t = w.thread; // 获取工作线程持有的线程实例
if (t != null) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock; // 使用全局可重入锁
mainLock.lock(); // 加锁,控制并发
try {
// Recheck while holding lock.
// Back out on ThreadFactory failure or if
// shut down before lock acquired.
int rs = runStateOf(ctl.get()); // 获取当前线程池状态
// 线程池状态为RUNNING或者(线程池状态为SHUTDOWN并且没有新任务时)
if (rs < SHUTDOWN ||
(rs == SHUTDOWN && firstTask == null)) {
if (t.isAlive()) // 检查线程是否处于活跃状态
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
workers.add(w); // 线程加入到存放工作线程的HashSet容器,workers全局唯一并被mainLock持有
int s = workers.size();
if (s > largestPoolSize)
largestPoolSize = s;
workerAdded = true;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock(); // finally块中释放锁
}
if (workerAdded) { // 线程添加成功
t.start(); // 调用线程的start()方法
workerStarted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (! workerStarted) // 如果线程启动失败,则执行addWorkerFailed方法
addWorkerFailed(w);
}
return workerStarted;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
# 添加worker失败
private void addWorkerFailed(Worker w) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (w != null)
workers.remove(w); // 线程启动失败时,需将前面添加的线程删除
decrementWorkerCount(); // ctl变量中的工作线程数-1
tryTerminate(); // 尝试将线程池转变成TERMINATE状态
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
final void tryTerminate() {
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
// 以下情况不会进入TERMINATED状态:
//(1)当前线程池为RUNNING状态
//(2)在TIDYING及以上状态
//(3)SHUTDOWN状态并且工作队列不为空
//(4)当前活跃线程数不等于0
if (isRunning(c) ||
runStateAtLeast(c, TIDYING) ||
(runStateOf(c) == SHUTDOWN && ! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return;
if (workerCountOf(c) != 0) { // 工作线程数!=0
interruptIdleWorkers(ONLY_ONE); // 中断一个正在等待任务的线程
return;
}
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
// 通过CAS自旋判断直到当前线程池运行状态为TIDYING并且活跃线程数为0
if (ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(TIDYING, 0))) {
try {
terminated(); // 调用线程terminated()
} finally {
ctl.set(ctlOf(TERMINATED, 0)); // 设置线程池状态为TERMINATED,工作线程数为0
termination.signalAll(); // 通过调用Condition接口的signalAll()唤醒所有等待的线程
}
return;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// else retry on failed CAS
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
# Worker源码解读
Worker是ThreadPoolExecutor类的内部类,此处只讲最重要的构造函数和run方法
private final class Worker extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer implements Runnable
{
// 该worker正在运行的线程
final Thread thread;
// 将要运行的初始任务
Runnable firstTask;
// 每个线程的任务计数器
volatile long completedTasks;
// 构造方法
Worker(Runnable firstTask) {
setState(-1); // 调用runWorker()前禁止中断
this.firstTask = firstTask;
this.thread = getThreadFactory().newThread(this); // 通过ThreadFactory创建一个线程
}
// 实现了Runnable接口的run方法
public void run() {
runWorker(this);
}
... // 此处省略了其他方法
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# runWorker方法
final void runWorker(Worker w) {
Thread wt = Thread.currentThread();
Runnable task = w.firstTask; // 获取工作线程中用来执行任务的线程实例
w.firstTask = null;
w.unlock(); // status设置为0,允许中断
boolean completedAbruptly = true; // 线程意外终止标志
try {
// 如果当前任务不为空,则直接执行;否则调用getTask()从任务队列中取出一个任务执行
while (task != null || (task = getTask()) != null) {
w.lock(); // 加锁,保证下方临界区代码的线程安全
// 如果状态值大于等于STOP且当前线程还没有被中断,则主动中断线程
if ((runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP) ||
(Thread.interrupted() &&
runStateAtLeast(ctl.get(), STOP))) &&
!wt.isInterrupted())
wt.interrupt(); // 中断当前线程
try {
beforeExecute(wt, task); // 任务执行前的回调,空实现,可以在子类中自定义
Throwable thrown = null;
try {
task.run(); // 执行线程的run方法
} catch (RuntimeException x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Error x) {
thrown = x; throw x;
} catch (Throwable x) {
thrown = x; throw new Error(x);
} finally {
afterExecute(task, thrown); // 任务执行后的回调,空实现,可以在子类中自定义
}
} finally {
task = null; // 将循环变量task设置为null,表示已处理完成
w.completedTasks++; // 当前已完成的任务数+1
w.unlock();
}
}
completedAbruptly = false;
} finally {
processWorkerExit(w, completedAbruptly);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# getTask方法
private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false; // 通过timeOut变量表示线程是否空闲时间超时了
// 无限循环
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get(); // 线程池信息
int rs = runStateOf(c); // 线程池当前状态
// 如果线程池状态>=SHUTDOWN并且工作队列为空 或 线程池状态>=STOP,则返回null,让当前worker被销毁
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount(); // 工作线程数-1
return null;
}
int wc = workerCountOf(c); // 获取当前线程池的工作线程数
// 当前线程是否允许超时销毁的标志
// 允许超时销毁:当线程池允许核心线程超时 或 工作线程数>核心线程数
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
// 如果(当前线程数大于最大线程数 或 (允许超时销毁 且 当前发生了空闲时间超时))
// 且(当前线程数大于1 或 阻塞队列为空)
// 则减少worker计数并返回null
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
try {
// 根据线程是否允许超时判断用poll还是take(会阻塞)方法从任务队列头部取出一个任务
Runnable r = timed ?
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r; // 返回从队列中取出的任务
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
总结一下哪些情况getTask()会返回null:
- 线程池状态为SHUTDOWN且任务队列为空
- 线程池状态为STOP、TIDYING、TERMINATED
- 线程池线程数大于最大线程数
- 线程可以被超时回收的情况下等待新任务超时
# 停止线程池
# 尝试中断tryTerminate()
final void tryTerminate() {
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
if (isRunning(c) ||
runStateAtLeast(c, TIDYING) ||
(runStateOf(c) == SHUTDOWN && ! workQueue.isEmpty()))
return;
if (workerCountOf(c) != 0) { // Eligible to terminate
// 中断 ONLY_ONE = false
interruptIdleWorkers(ONLY_ONE);
return;
}
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
if (ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(TIDYING, 0))) {
try {
terminated();
} finally {
ctl.set(ctlOf(TERMINATED, 0));
termination.signalAll();
}
return;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// else retry on failed CAS
}
}
private void interruptIdleWorkers(boolean onlyOne) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
for (Worker w : workers) {
Thread t = w.thread;
if (!t.isInterrupted() && w.tryLock()) {
try {
// 前面已经被中断了,中断别人,相当于链式的中断
t.interrupt();
} catch (SecurityException ignore) {
} finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
if (onlyOne)
break;
}
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
# 唤醒getTask()
private Runnable getTask() {
boolean timedOut = false; // Did the last poll() time out?
for (;;) {
int c = ctl.get();
int rs = runStateOf(c);
// Check if queue empty only if necessary.
if (rs >= SHUTDOWN && (rs >= STOP || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
decrementWorkerCount();
return null;
}
int wc = workerCountOf(c);
// Are workers subject to culling?
boolean timed = allowCoreThreadTimeOut || wc > corePoolSize;
if ((wc > maximumPoolSize || (timed && timedOut))
&& (wc > 1 || workQueue.isEmpty())) {
if (compareAndDecrementWorkerCount(c))
return null;
continue;
}
try {
// 抛出异常会重置状态
Runnable r = timed ?
workQueue.poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) :
workQueue.take();
if (r != null)
return r;
timedOut = true;
} catch (InterruptedException retry) {
timedOut = false;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
如果直接使用shutdown函数
如果线程被中断会立即停止该线程在执行的任务吗?
interrupt() 方法并不像在 for 循环语句中使用 break 语句那样干脆,马上就停止循环。调用 interrupt() 方法仅仅是在当前线程中打一个停止的标记,并不是真的停止线程。
← Threadlocal JS开发技巧 →

